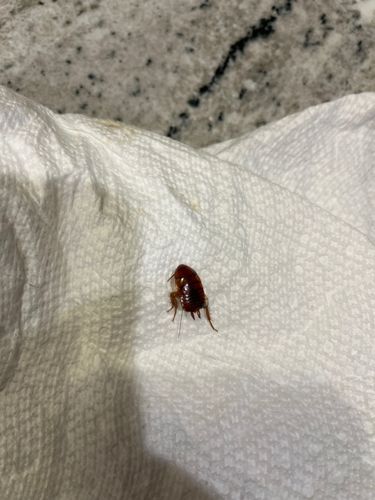
Cockroach (likely American or Oriental Cockroach nymph based on appearance)
Scientific Name: Periplaneta americana (American) or Blatta orientalis (Oriental) - nymph
Order & Family: Blattodea (Order), Blattidae (Family) - likely for American or Oriental
Size: Nymphs vary in size from a few millimeters (first instar) up to 2-3 cm for later instars before reaching adult size (3-5 cm for adults).
Natural Habitat
Warm, humid, and dark environments, often indoors in kitchens, bathrooms, basements, sewers, and drains. Also found outdoors in dark, moist areas under debris, rocks, or wood.
Diet & Feeding
Omnivores, scavenging on a wide range of organic matter including food scraps, decaying matter, starches, sweets, grease, pet food, paper, fabric, and even other dead insects. They are opportunistic feeders.
Behavior Patterns
Nocturnal and highly sensitive to light, preferring to hide in cracks and crevices during the day. They are social insects that live in groups and are known for their rapid reproduction. Nymphs undergo several molts (instars) before reaching adulthood. They are agile runners and can quickly scurry away when disturbed.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Cockroaches are considered pests. They can spread bacteria and pathogens (e.g., Salmonella, E. coli) picked up from rotting food or sewage, potentially contaminating food preparation surfaces and stored food. They can also trigger allergies and asthma in sensitive individuals due to their shed skins and droppings. Benefits: In natural ecosystems, some cockroach species play a role as decomposers, helping to break down decaying organic matter. However, the species found indoors are almost exclusively pests.
Identified on: 9/11/2025