Mosquito
Scientific Name: Various species, common genera include *Aedes*, *Anopheles*, *Culex*
Order & Family: Order: Diptera, Family: Culicidae
Size: Typically 3 to 6 mm (0.12 to 0.24 inches) in length, though some species can be larger or smaller.
Natural Habitat
Mosquitoes are found globally, except in Antarctica. They thrive in warm, humid environments and require standing water for their larval and pupal stages. Habitats include swamps, marshes, ponds, ditches, puddles, and artificial containers holding water like tires, buckets, and bird baths.
Diet & Feeding
Adult female mosquitoes feed on blood (hematophagy) from mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians, depending on the species. Both male and female mosquitoes feed on nectar and other plant sugars for energy.
Behavior Patterns
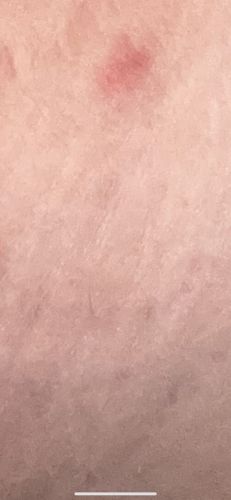
As the image appears to show a skin reaction, likely a bite, the behavior pattern described is that of the biting insect. Mosquitoes are most active during dawn and dusk, though some species bite during the day. Females bite to obtain a blood meal necessary for egg development. They are attracted to carbon dioxide, body heat, and certain chemicals on human skin. Bites typically result in an immediate itchy welt.
Risks & Benefits
Potential Risks: Mosquitoes are significant vectors for numerous diseases including Malaria, Dengue fever, Chikungunya, Zika virus, West Nile virus, and various types of encephalitis. Bites can also cause localized allergic reactions leading to itching, swelling, and redness. Potential Benefits: Mosquito larvae and adults serve as food sources for various animals like fish, birds, and other insects. Adult mosquitoes also play a role in pollination, particularly for certain orchid species.
Identified on: 9/4/2025