Human Scabies Mite
Scientific Name: Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis
Order & Family: Order: Sarcoptiformes, Family: Sarcoptidae
Size: 0.30 to 0.45 mm long for females; males are about half that size.
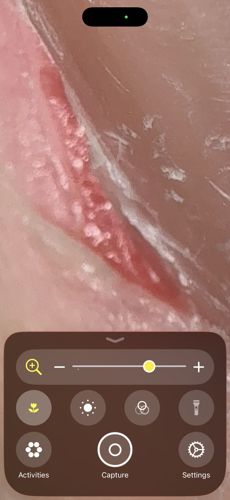
Natural Habitat
The epidermis (outer layer) of human skin, specifically creating burrows in areas like finger webs, wrists, and elbows.
Diet & Feeding
They feed on human skin cells and extracellular fluid found within the epidermis.
Behavior Patterns
The female mite burrows into the skin to lay eggs. They are microscopic and move slowly under the skin, often causing intense itching that worsens at night.
Risks & Benefits
They cause Scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation characterized by severe itching and rashes. If left untreated, scratching can lead to secondary bacterial infections like impetigo or cellulitis. They provide no ecosystem benefits to humans.
Identified on: 12/28/2025