Tunga penetrans (Chigoe flea / Jigger)
Scientific Name: Tunga penetrans
Order & Family: Order: Siphonaptera, Family: Tungidae
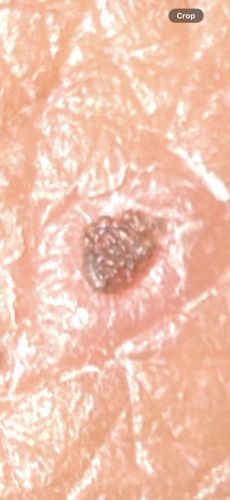
Size: Before feeding: approximately 1mm. After burrowing and becoming gravid: can expand to 5-10mm (about the size of a pea).
Natural Habitat
Found in tropical and subtropical regions, particularly in sandy soil, floors of houses, and livestock stables in sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, and the Caribbean.
Diet & Feeding
Hematophagous (feeds on blood). Males and non-gravid females feed intermittently; the mated female burrows into the host's skin to feed continuously.
Behavior Patterns
The female flea burrows into the skin of a host (usually the feet). Once inside, she remains permanently embedded to feed and produce eggs, causing a localized lesion. After about two weeks, she releases hundreds of eggs through a small opening in the skin and eventually dies.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Causes tungiasis, characterized by intense inflammation, pain, and itching. Secondary infections like cellulitis, tetanus, or gangrene can occur. There are no known benefits to humans or the ecosystem; it is considered a parasitic pest.
Identified on: 1/3/2026