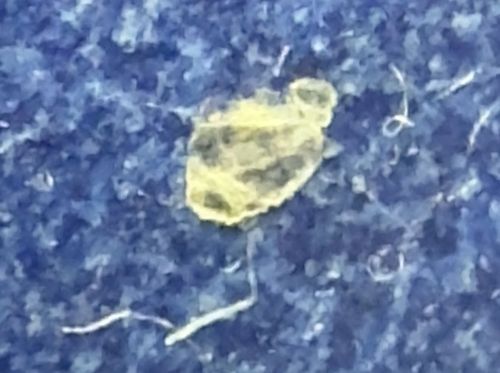
Casemaking Clothes Moth Larva (specifically the larval case)
Scientific Name: Tinea pellionella
Order & Family: Lepidoptera: Tineidae
Size: Larval case is typically 5-10 mm (approx. 1/4 to 3/8 inch) long.
Natural Habitat
Indoor environments, particularly dark areas like closets, drawers, under carpets, and in storage boxes where natural fibers are present.
Diet & Feeding
Keratin-based materials such as wool, fur, silk, feathers, felt, and hair. They can also feed on lint, dust, and food debris.
Behavior Patterns
The larva constructs a portable, flattened, tubular case out of silk and debris (fibers, sand, etc.) which it carries around for protection. It never leaves this case while feeding, extending only its head and legs to move and eat. When ready to pupate, it seals the ends of the case.
Risks & Benefits
Risks: Significant pest of textiles. They damage clothing, carpets, upholstery, and stored fabrics by eating holes in them. Benefits: In nature, they act as recyclers of organic matter (like animal carcasses and feathers), but are considered purely pests in homes.
Identified on: 2/14/2026