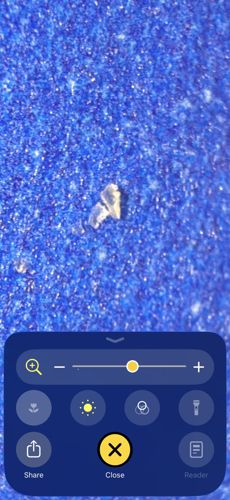
Human Head Louse (Egg/Nit Shell)
Scientific Name: Pediculus humanus capitis
Order & Family: Order: Psocodea (formerly Phthiraptera), Family: Pediculidae
Size: Nits are approximately 0.8 mm long; adults are 2-3 mm long.
Natural Habitat
Found exclusively on the human scalp, typically attaching eggs (nits) to hair shafts close to the scalp for warmth.
Diet & Feeding
Obligate ectoparasites that feed exclusively on human blood several times a day.
Behavior Patterns
Lice cannot jump or fly; they move by crawling. Eggs are glued to hair with a specialized cement. They undergo incomplete metamorphosis (egg, nymph, adult).
Risks & Benefits
Causes intense itching (pediculosis) and scalp irritation due to an allergic reaction to saliva. While a nuisance and highly contagious through head-to-head contact, they do not transmit diseases.
Identified on: 1/2/2026