Louse / Head Louse (Nymph/Egg stage)
Scientific Name: Pediculus humanus capitis
Order & Family: Order: Psocodea (formerly Phthiraptera), Family: Pediculidae
Size: 0.5 mm to 3 mm (Nits/eggs are approximately 0.8 mm)
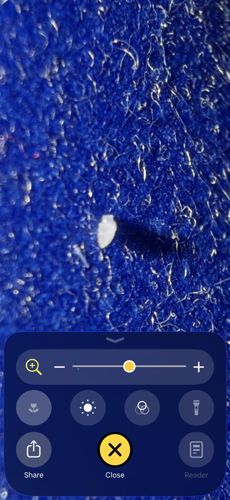
Natural Habitat
Human scalp and hair; they are obligate ectoparasites and cannot survive for long away from a human host.
Diet & Feeding
Hematophagous (feeds exclusively on human blood several times a day).
Behavior Patterns
They are wingless and crawl between hairs; they cannot jump or fly. Females lay eggs (nits) and glue them to hair shafts near the scalp. They undergo hemimetabolous metamorphosis from egg to nymph to adult.
Risks & Benefits
Risks include intense itching (pruritus) due to allergic reactions to saliva, scalp irritation, and potential secondary bacterial infections from scratching. Unlike body lice, head lice are not known to spread diseases. Benefit: None to the host; they are purely parasitic.
Identified on: 1/11/2026